Heart failure treatment is essential for managing this condition, which affects millions of people worldwide. Heart failure, sometimes referred to as congestive heart failure, occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Treatment is crucial for improving quality of life and preventing further complications. Heart failure treatment includes medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical interventions.
There are different types of heart failure, and the treatment approach will vary based on the type and severity of the condition. In this article, we will explore various aspects of heart failure, such as its types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and the available treatment options. Chronic heart failure symptoms can vary from mild to severe, and early detection is key to managing the condition. Understanding heart failure and its treatment can help individuals lead a healthier life.
What is Heart Failure?
Heart failure is a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently to meet the body’s demands. This can lead to fatigue, fluid retention, and shortness of breath. Chronic heart failure symptoms may appear gradually and worsen over time. The condition can result from various factors such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, or previous heart attacks.
The heart is a muscular organ that needs to work efficiently to pump blood throughout the body. When the heart fails to pump effectively, the body does not get enough oxygen and nutrients, which can lead to various complications. In some cases, heart failure can be managed with heart failure treatment, such as medications and lifestyle changes. It is important to seek early intervention and follow the prescribed heart failure treatment plan to prevent the condition from worsening.
Types of Heart Failure
There are several types of heart failure, each affecting the heart in different ways. The two main types are:
- Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF): The heart’s left ventricle loses its ability to contract and pump blood. This is the most common form of heart failure.
- Diastolic Heart Failure (HFpEF): The heart muscle stiffens and cannot relax properly, preventing the heart from filling with blood. This type is more common in older adults.
Other types include right-sided heart failure, where the right side of the heart cannot pump blood efficiently to the lungs, and congestive heart failure, which involves fluid build-up in the body. Treatment options vary for each type, but heart failure treatment typically involves medications, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery.
Heart Failure Signs and Symptoms
Heart failure symptoms can be mild or severe and vary based on the type and stage of heart failure. Common signs of heart failure include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or when lying down
- Fatigue or weakness
- Swelling in the ankles, legs, or abdomen
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Persistent cough or wheezing
- Weight gain due to fluid retention
The presence of chronic heart failure symptoms requires timely medical attention. Early detection and heart failure treatment can help manage these symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, doctors may recommend medications, lifestyle changes, or other interventions to alleviate the effects of heart failure.
Causes
Heart failure can develop due to various underlying conditions. The most common causes include:
- Coronary artery disease: Blocked or narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the heart.
- High blood pressure: Over time, high blood pressure can cause the heart to weaken.
- Previous heart attacks: Damage from heart attacks can impair the heart’s ability to pump.
- Valvular heart disease: Damaged heart valves can disrupt blood flow.
- Cardiomyopathy: A disease of the heart muscle that weakens its function.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can contribute to heart disease and heart failure.
Proper heart failure treatment targets the underlying causes and helps prevent further damage to the heart. In some cases, treating conditions like high blood pressure and coronary artery disease can reduce the progression of heart failure.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing heart failure involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, and tests. A healthcare provider will ask about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and risk factors. Some common diagnostic tests for heart failure treatment include:
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart’s structure and function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the heart’s electrical activity to check for arrhythmias or damage.
- Blood tests: Measure markers such as B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), which helps determine heart failure severity.
- Chest X-ray: Looks for signs of fluid in the lungs or an enlarged heart.
In cases of treatment of anemic heart failure, blood tests are also crucial for determining red blood cell levels. Proper diagnosis is the first step in creating an effective heart failure treatment plan.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the development of heart failure, including:
- Age: The risk increases with age, particularly for those over 65.
- High blood pressure: Long-term hypertension strains the heart and increases the risk of heart failure.
- Coronary artery disease: Reduced blood flow to the heart increases heart failure risk.
- Diabetes: A history of diabetes can damage blood vessels and the heart.
- Family history: A family history of heart disease or heart failure can increase your risk.
- Lifestyle factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption contribute to heart disease.
Identifying these risk factors allows for preventive measures, and heart failure treatment can be tailored to individuals with these risk factors.
Prevention
Preventing heart failure involves addressing the underlying conditions and adopting a healthy lifestyle. Key prevention strategies include:
- Controlling blood pressure: Regular monitoring and treatment of high blood pressure reduce the risk.
- Managing cholesterol levels: Lowering cholesterol with diet and medication can prevent coronary artery disease.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Preventing obesity helps reduce strain on the heart.
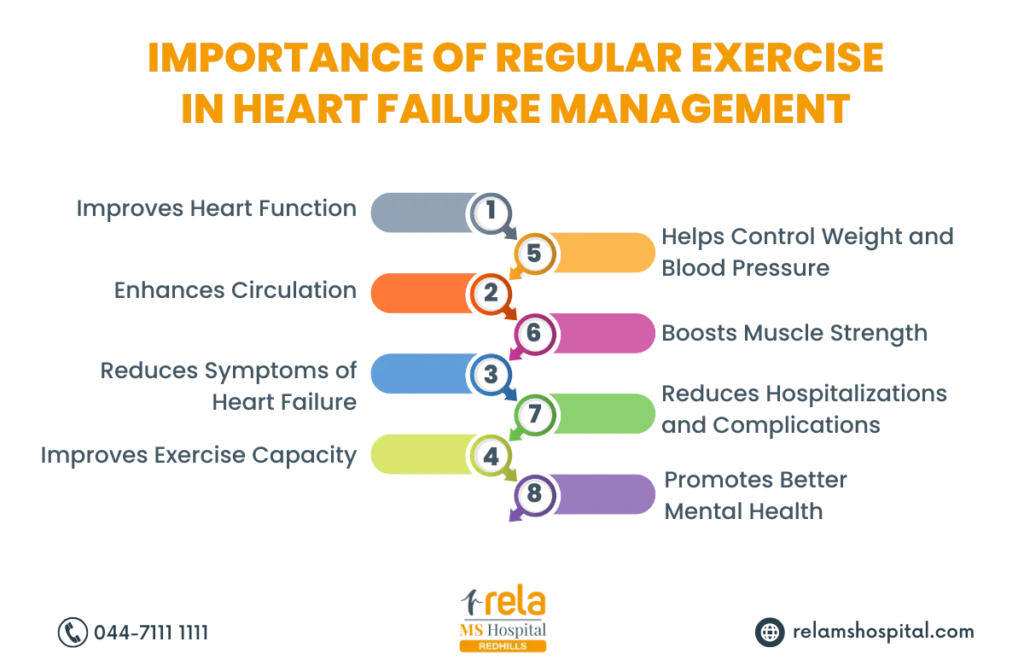
- Regular exercise: Engaging in moderate physical activity strengthens the heart.
- Healthy diet: Eating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports heart health.
- Avoiding smoking and excess alcohol: Smoking and heavy drinking contribute to heart disease.
By addressing these factors, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of heart failure and maintain heart health. Proper heart failure treatment also plays a role in preventing further complications.
Treatment Options
Heart failure treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include:
- Medications: ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and other medications help manage heart failure symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a low-sodium diet, and weight management are important for managing heart failure.
- Surgical options: In some cases, surgery may be required to repair heart valves, bypass blocked arteries, or implant a pacemaker or defibrillator.
- Heart transplant: In severe cases, a heart transplant may be necessary for those who don’t respond to other treatments.
The treatment of anemic heart failure involves addressing both the heart condition and the underlying anemia. Combining these treatments can improve symptoms and quality of life for heart failure patients.
Healthy Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can greatly impact heart failure treatment. Key lifestyle recommendations include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet: Eating foods rich in nutrients and low in sodium supports heart function.
- Getting regular exercise: Light to moderate exercise helps maintain heart strength.
- Avoiding alcohol and smoking: Both smoking and excessive alcohol contribute to heart disease.
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can worsen heart failure symptoms, so stress management techniques like meditation or yoga are beneficial.
By incorporating these changes, heart failure patients can significantly improve their heart function and reduce the impact of chronic heart failure symptoms.
Procedures and Surgeries
For some heart failure patients, procedures and surgeries may be necessary. Common procedures include:
- Coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG): This surgery restores blood flow to the heart.
- Heart valve repair or replacement: Repairing or replacing damaged heart valves can improve heart function.
- Pacemaker or defibrillator implantation: These devices help regulate the heart’s rhythm and prevent sudden cardiac arrest.
- Heart transplant: A heart transplant may be the only option for those with severe heart failure who do not respond to other treatments.
These procedures aim to improve heart function and provide relief from heart failure symptoms. Heart failure treatment can also involve a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments to ensure the best outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heart failure treatment is essential for managing the condition and improving quality of life. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for addressing chronic heart failure symptoms and reducing the risk of complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals with heart failure can take proactive steps to manage their condition. Whether through medications, lifestyle changes, or surgery, effective heart failure treatment can help individuals lead a more active and healthier life.





